
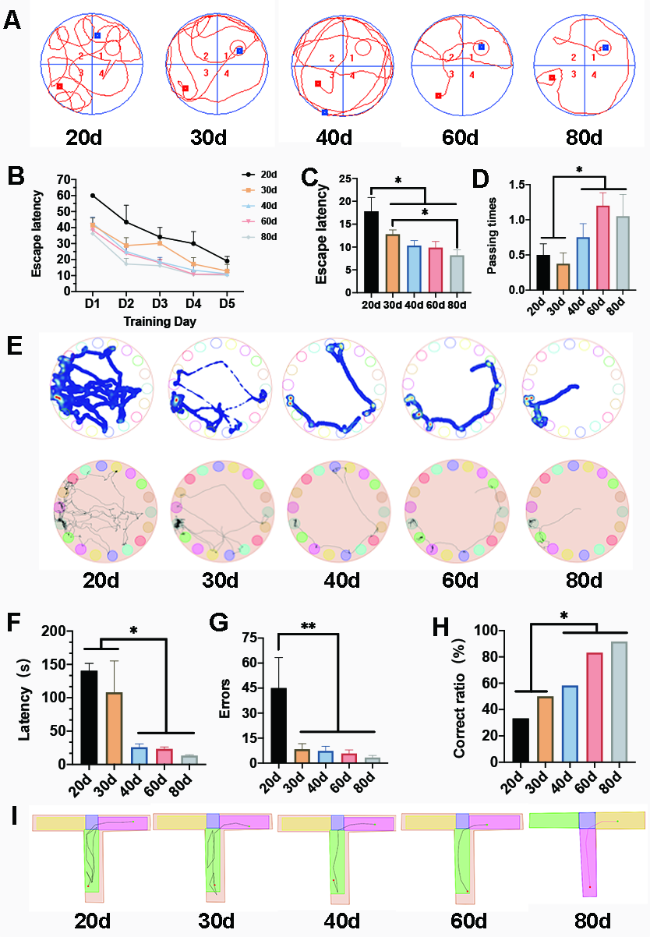
The procedure, technique, and end point for testing learning and memory were followed as per the parameters described earlier. Models Employed for Evaluation of Memory Enhancing Activity in Mice 2.5.1. Injection of diazepam was diluted in normal saline.Ģ.5.

Scopolamine hydrobromide was dissolved in normal saline. Palmatine was suspended in 10% Tween 80 in normal saline. Selection of Dosesĭoses of various drugs were selected on the basis of literature, that is, 0.4 mg/kg for scopolamine, 1 mg/kg for diazepam, 0.1 mg/kg for physostigmine, 0.1 and 1 mg/kg for palmatine. Louis, USA) physostigmine, acetylcholine iodide, acetylthiocholine iodide, and 5,5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (Hi-Media Laboratories, Mumbai) diazepam (Calmpose injection, Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd., Gurgaon, India). Palmatine and scopolamine hydrobromide (Sigma-Aldrich, St. The experimental protocol was approved by Institutional Animals Ethics Committee (IAEC) and animal care was taken as per the guidelines of Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India (Registration no. The animals were acclimatized for at least five days before behavioural experiments which were carried out between 09:00 and 17:00 h.
The animals were kept fasted 2 h before and 2 h after drug administration.
#ANY MAZE LATENCY TO ESACPE FREE#
The animals had free access to food and water. Animals were housed separately in groups of 8 per cage (Polycarbonate cage size: cm) under laboratory conditions with alternating light and dark cycle of 12 h each. Since estrogens (female sex hormones) have been found to have effect on memory, we excluded female mice and used only male mice for the study. Swiss male albino mice, weighing around 20–25 g, were purchased from Disease Free Small Animal House, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar (Haryana). So the present study was designed to investigate the effect of palmatine on the learning and memory of mice by employing behavioral models. Thus, palmatine has potential for the management of dementia. It has been also shown to be inhibitor of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE 1), acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterases. Palmatine has been reported to possess sedative and antioxidant activities. It is typically yellow in color and is an active constituent of a number of plants, such as Coptidis rhizoma, and so forth. Palmatine is a quaternary protoberberine alkaloid. The imbalance between the generation of free radicals and antioxidants has also been claimed to be a cause of AD. One of the major therapeutic strategies is to inhibit the AChE, and hence, to increase the acetylcholine level in the brain. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) plays a key role in the regulation of the cholinergic system and hence, inhibition of AChE has emerged as one of the most promising strategies for the treatment of AD.

The primary causes of AD appear to be (i) decreased cholinergic activity (ii) deposition of amyloid-beta peptides in the brain (iii) oxidative stress. AD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive and memory deterioration, progressive impairment of activities of daily living, and a multiplicity of behavioural and psychological disturbances. Introductionĭementia, the commonest form (accounting for approximately 60% of all cases) of which is Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mainly affects older people and it is estimated that, by 2050, more than 115 million people will have dementia. Thus, palmatine showed memory-enhancing activity in mice probably by inhibiting brain acetylcholinesterase activity, through involvement of GABA-benzodiazepine pathway, and due to its antioxidant activity. Palmatine and physostigmine also significantly reduced brain acetylcholinesterase activity of mice. Palmatine (1 mg/kg) significantly reversed scopolamine- and diazepam-induced amnesia in mice. Memory-enhancing activity of palmatine (1 mg/kg) was comparable to physostigmine. The drugs did not show any significant effect on locomotor activity of the mice.
#ANY MAZE LATENCY TO ESACPE PLUS#
Palmatine (0.5 and 1 mg/kg) and physostigmine significantly improved learning and memory of mice, as indicated by decrease in transfer latency using elevated plus maze, and decrease in escape latency during training and increase in time spent in target quadrant during retrieval using Morris water maze. Effect of palmatine on scopolamine- and diazepam-induced amnesia was also investigated. Brain acetylcholinesterase activity was also estimated. Effect of drugs on learning and memory of mice was evaluated using elevated plus maze and Morris water maze. Palmatine (0.1, 0.5, 1 mg/kg, i.p.) and physostigmine (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) per se were administered for 10 successive days to separate groups of mice.
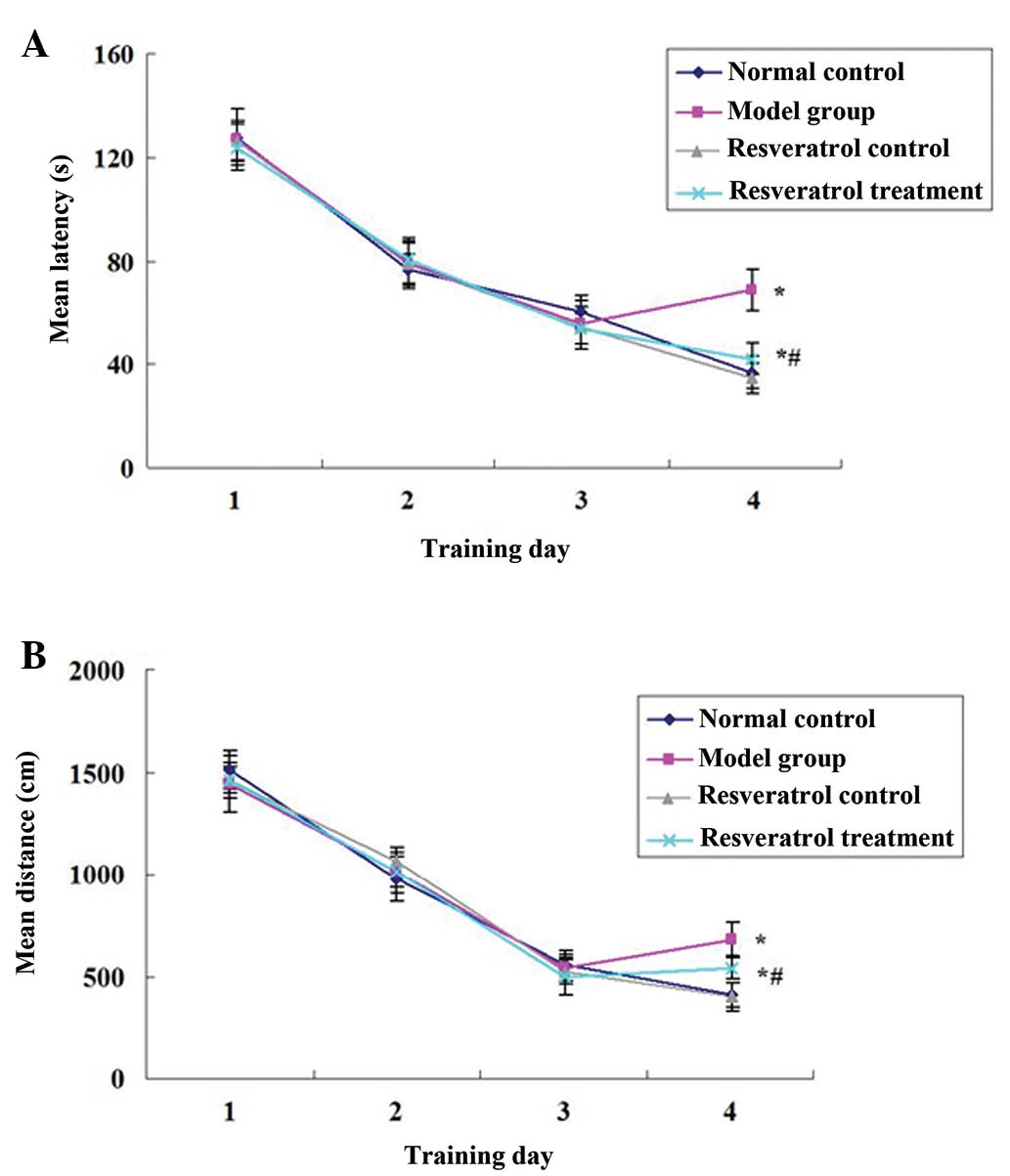
The present study was designed to evaluate the effect of palmatine on memory of Swiss young male albino mice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
